This article is related to Dodo v0.8. In version 0.9.0 and later, CSP issues have been resolved.
Content Security Policy (CSP)
Content Security Policy (CSP) is a security standard that allows website owners to control which resources can be loaded by a webpage. It helps prevent attacks like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) by specifying trusted sources for scripts, stylesheets, images, and frames. CSP also includes a reporting mechanism to track and address policy violations, enhancing the security posture of web applications.
SOME EXAMPLES
1. **Example 1: Block Inline Scripts and Styles**
- Explanation: Using CSP, you can prevent inline scripts and styles from executing within your webpage, reducing the risk of XSS attacks.
- CSP Directive: `script-src 'self'; style-src 'self';`
2. **Example 2: Allow Scripts from Specific Domains**
- Explanation: You can specify trusted domains from which scripts can be loaded, limiting the risk of executing malicious code from untrusted sources.
- CSP Directive: `script-src 'self' trustedscripts.com;`
3. **Example 3: Report Violations to a URL**
- Explanation: Configure CSP to report policy violations to a specified URL, enabling you to monitor and address security issues proactively.
- CSP Directive: `report-uri /csp-report-endpoint`
Blocked JS Functions
- eval()
- Function()
- setTimeout()
- setInterval()
- setImmediate()
- execScript()
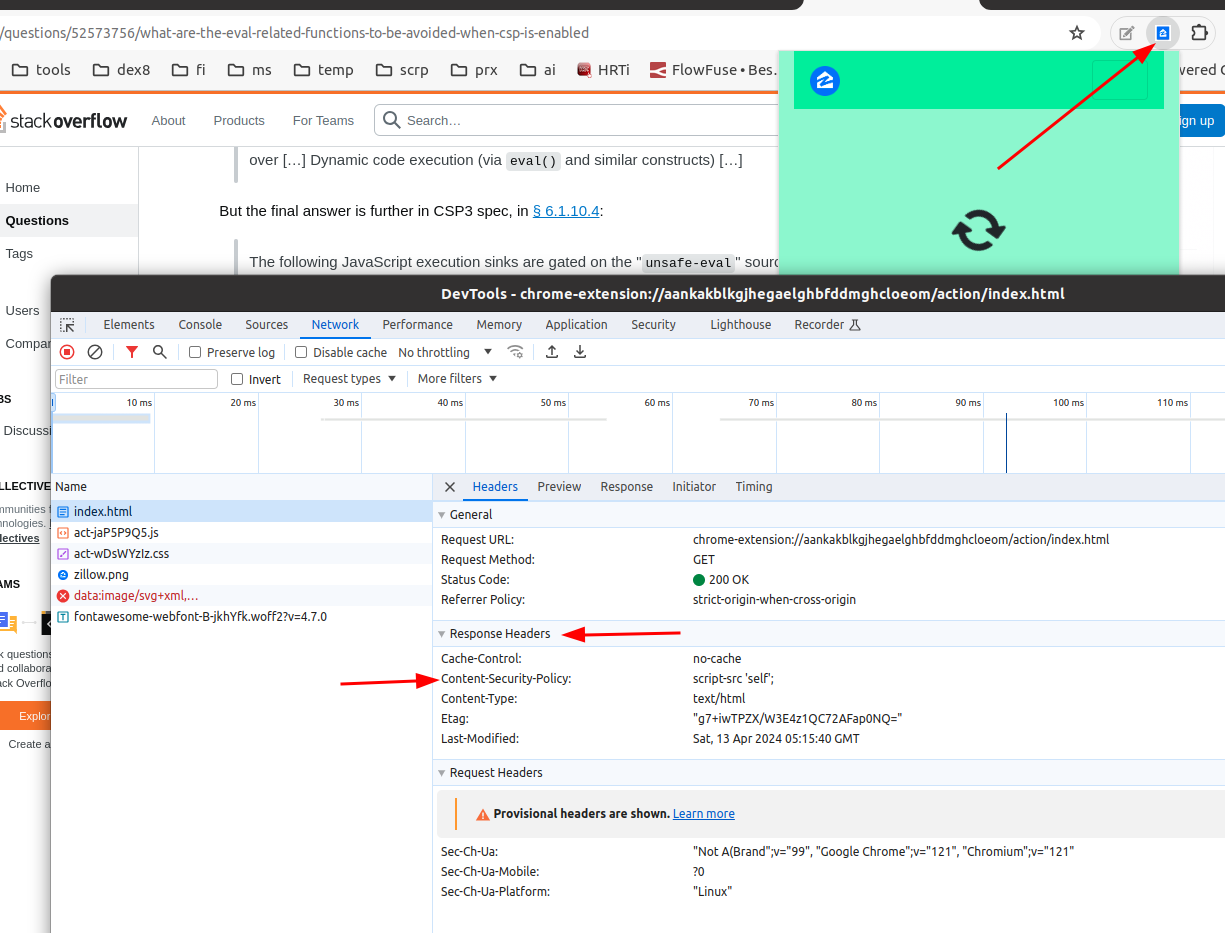
CSP in Chrome Extension
CSP in the chrome extension Manifest v3 is always:Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self';
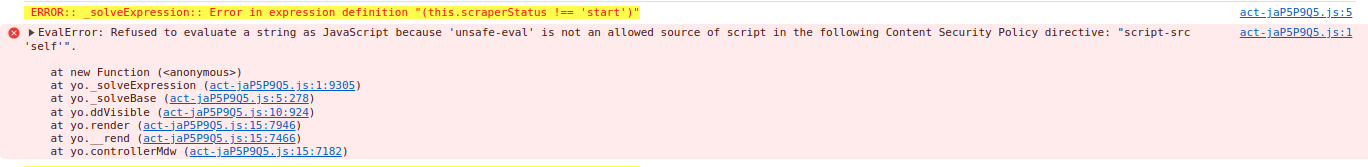
what blocka functions like eval(9, Function(), ... with error
EvalError: Refused to evaluate a string as JavaScript because 'unsafe-eval' is not an allowed source of script in the following Content Security Policy directive: "script-src 'self'".